Find out
The ability of Word to open and save files as plain text in a variety of different encodings enables you to convert a file whose characters are encoded in one scheme into a file using a different encoding scheme. It also provides a way of identifying which encoding scheme has been used to encode a piece of text.
This can be very useful, especially when dealing with information gleaned from the Internet where older schemes are prevalent. Otherwise it can be used to convert files which have been created by non-Unicode applications. By converting such files into Unicode you may increase the number of applications that can handle the data therein.
In order to convert between character encodings:
Open the file in Word by selecting Open from the File menu. Word will probably identify the current encoding correctly
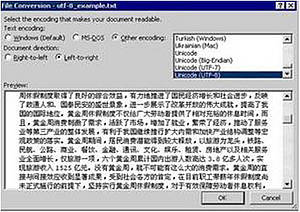
If you are sure that a different encoding scheme has been used for the file you are about to open, you can override Word’s suggestion using the File Conversion dialog box which opens automatically
Once you have opened the file successfully, simply save it as plain text as described in topic 19. Make sure you select the encoding into which you wish to convert your data.
Why is this information important for translators and translation teachers?
Since character encoding depends on the language (languages use different characters, for example, there are different alphabets, as well as languages that are read from left to right or right to left or horizontally or vertically) and dealing with the language is the work of translators, they should know not only what different character encoding types exist, but also how to apply them.
Especially when translators work with several languages at the same time, they need to change character encodings in order to display them correctly on the same page or in the document. One of the most commonly used character encodings by translators is the Unicode encoding standard, as it supports all languages. It is increasingly used by software applications and allows users to exchange data without having to worry about compatibility issues.
Working with different character encodings is very important especially in the translation of web pages and software localization in general.

