Find out
Saving a file as plain text means that the textual content of the document is saved as a series of character codes.
Documents saved in this way will lose all but the most basic formatting information. Tabs and paragraph breaks will be preserved because these features are encoded as characters.
To save a file as plain text:
- Select Save as from the File menu
- Then choose Plain Text from the Save as type drop-down list.
- Change the file name if you wish
- Press the Save button
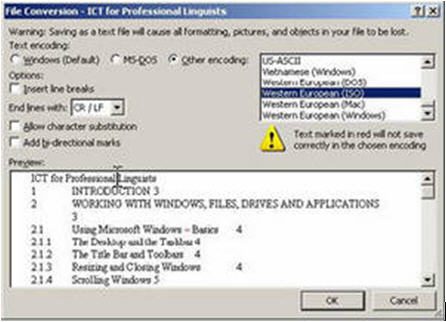
- Next you will be presented with a File Conversion dialog box
- Here you can choose from a number of options that control the type of plain text file that is saved
- By default, the file will be saved using a proprietary Windows character encoding scheme
- Unicode (UTF-8), US-ASCII, and a range of other encoding schemes can be selected from the Other Encoding menu (Note that choosing “Unicode” will mean that UTF-16 is used)
- The Other Encoding menu can be activated by pressing the small radio button next to it
Word will sometimes warn you that: "Text marked in red will not save correctly in the chosen encoding". This happens when the character encoding scheme you have chosen does not support characters used in the file. While such advice can be helpful, you should not assume that all the characters used in your document are supported simply because you have not been warned!
Subject to the character encoding used, it is possible to edit and manipulate the content of the resulting plain text in any number of different programs. These include basic text editors, such as Microsoft Notepad, as well as specialist applications, such as those used in translation projects.
Why is this information important for translators and translation teachers?
Because of their flexibility - text files can contain large amount of information without becoming too large, can be opened and read on almost any platform, store few metadata elements, among others -, text files are used very often when exporting or importing data from one software application to another one.
Translators need to know how to convert different types of files – e.g. Word files – into text files in order to be able to work with special translation software such as terminology databases, translation memories, etc.

