Though in the previous section we gave an overview of the types of localisation file formats that exist, we will now focus on software localisation file formats, and particularly on the localisable elements contained in those formats.
Localisable elements in software localisation file formats (source code files or binary files) are those data which make up the software user interface. The following are examples of user interface elements to be localised:
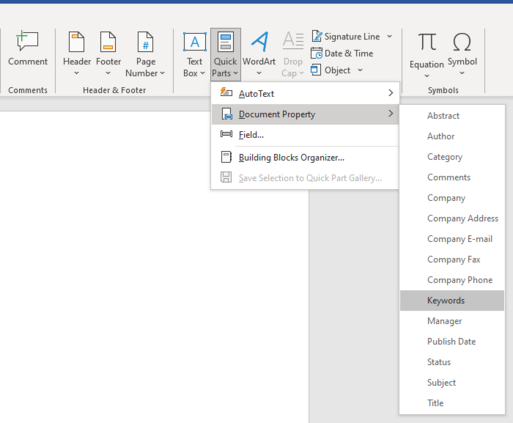
Also called hotkeys, access keys are sequences of key strokes that allow users to access functions in menus and submenus. Access keys are commonly represented by a mnemonic, usually the initial letter of the function. This is underlined on the menu line – e.g. "Save".
Shortcuts are also keyboard combinations used to access functions in menus and submenus. The key combination is an abbreviation of the menu item command. In our example Ctrl+S is used as accelerator key combination for the Save command. When a software application is localised, shortcuts are usually not changed, mainly because they are very often common to many applications. Access keys, however, have to be adapted to the names of the respective options in the target language.
These could be:
- Bitmaps: This is the type of format that graphics usually have in a software user interface. Cursors and icons, for example, can come in bitmap format. Bitmaps need to be localised and this can be done using a common graphic editor such as Adobe Photoshop or JASC Paint Shop Pro.
- Icons: These are small pictures on the computer screen representing objects or functions for the user. Their purpose is to make the use of computers easier, and are a feature of graphical user interface (GUI) systems.
- Cursors: A cursor is the symbol on computer screens that indicates the current entry position or where the next character is going to appear.