You can import one or several translation memories into your existing one, in order to increase the chaces of getting relevant matches.
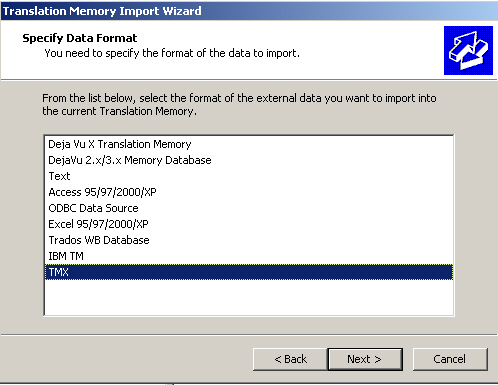
Translation memories can be imported from specific formats and exported into several different formats, such as TXT, etc. The standard import and export format is the Translation Memory eXchange (TMX) which will be discussed in the section Exchanging TMs.
When importing databases between different TM applications, the TMX-format functions as a standard exchange format. Another file format widely used when importing databases are tab-delimited .txt files. Both of these situations may apply when when you want to import the result of an alignment process into a TM.
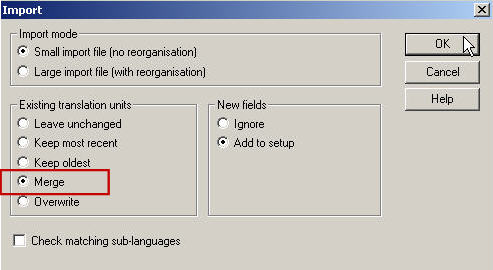
Merge option
During the import process you can also specify whether you want to merge the imported entries with the existing ones in the database (e.g. in Trados).
Duplicate segments are similar source segments which are found both in the existing and the imported TM. Depending on the system you are using, duplicate source segments can be handled differently. For example, in DVX, the duplicate segments are simply imported as new segments. This can happen in Trados as well. Nevertheless, the Trados user has an extra function, called Do not allow multiple translations. By using this function, the new imported translation for the duplicate segment overwrites the one that exists in the TM into which the import is executed.
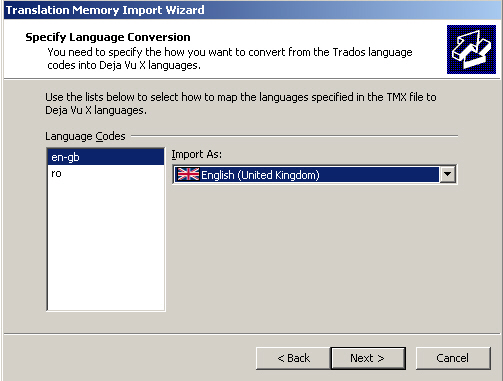
When importing databases within different TM applications, it is also necessary to specify the language variety of the TMX file, since TM systems may use different language codes. The following graphic shows the language conversion step necessary for importing a TMX file created in Trados into a TM created in Déjà Vu.