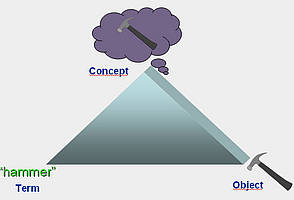
Le Triangle sémiotique proposé pour la première fois en 1923 par les linguistes américains Ogden et Richards est l'une des représentation les plus claires et concises de la relation existante entre l'objet (ou référent), le concept (ou référence) et le terme (ou symbole).
Les éléments du triangle sémiotique peuvent être définis de la manière suivante :
- Objet ou référent : "any part of the perceivable or conceivable world." [ISO 1087] Certains référents peuvent être matériels (par exemple une maison précise, la Tour Eiffel) ou immatériels (la vitesse, la douleur, la liberté...). [cf : adapté de DIN 2330, p. 3]
- Concept ou référence : "A unit of thought constituted through abstraction on the basis of properties common to a set of objects. The semantic content of a concept can be re-expressed by a combination of other and different concepts, which may vary from one language or culture to another". [ISO 5963:1985]
- Terme ou symbole : "Designation of a defined concept in a special language by a linguistic expression." [ISO 1087]

